
Sterility testing ensures the safety of products by detecting microbial contamination. Per the traditional compendial methodology described in USP <71>, product samples are incubated in growth media for 14 days, allowing any contaminants to grow after the initial inoculation or filtering part of the sterility test is performed in a cleanroom or isolator. However, for many products there is also the option of rapid sterility testing using rapid microbiological methods (RMMs). Rapid sterility testing using RMMs can deliver the incubation results in approximately 6 days (compared to 14 days).
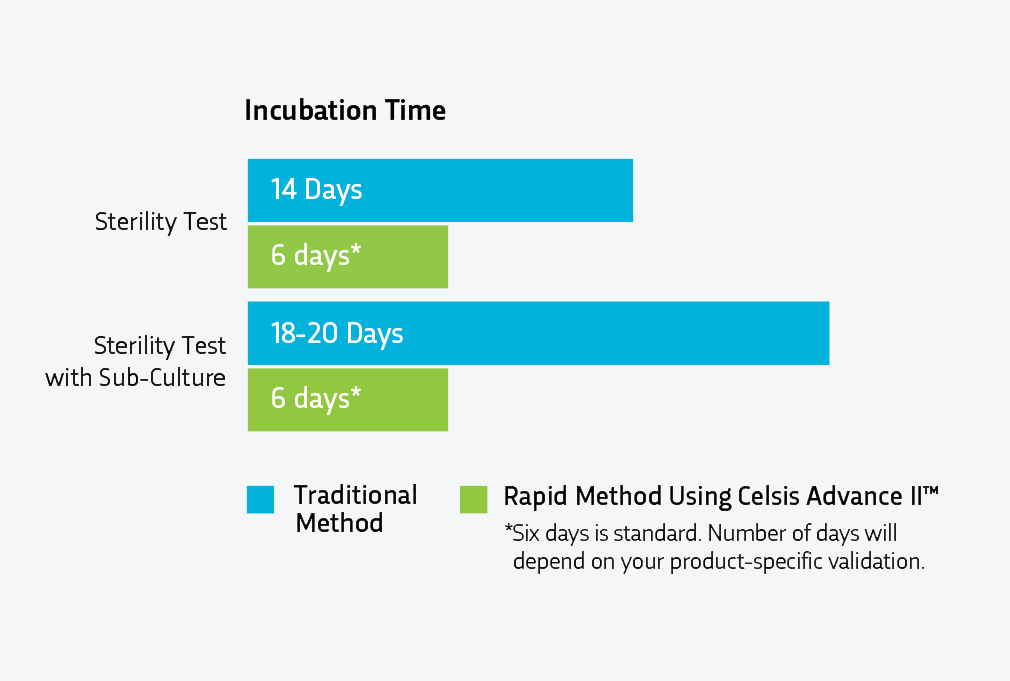 Rapid sterility testing uses advanced bioluminescence technology to detect microbial adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In this process, through Celsis Advance II™ technology, light is produced at elevated levels to indicate microbial contamination. Because this is done through instrumentation, subjective visual checks for turbidity (the indicator of contamination) are replaced by an instrument’s quantitative results. This method reduces the testing time to at least half the time required by the traditional compendial method.
Rapid sterility testing uses advanced bioluminescence technology to detect microbial adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In this process, through Celsis Advance II™ technology, light is produced at elevated levels to indicate microbial contamination. Because this is done through instrumentation, subjective visual checks for turbidity (the indicator of contamination) are replaced by an instrument’s quantitative results. This method reduces the testing time to at least half the time required by the traditional compendial method.
Rapid testing for product sterility is useful for a broad range of product types that can be tested by membrane filtration or direct inoculation. It is ideal for products that have limited shelf lives, that require prompt release to market, or that are manufactured in small batches. With the Celsis Advance II™ technology this testing has a high capacity for throughput and is simple to perform.
This test complies with GMP and general sterility guidance found in USP <71>, Ph. Eur. 2.6.1, and JP 4.06 as well as guidance specifically for alternative methods, found in USP <1223>, PDA TR33, and Ph. Eur. 5.1.6.


